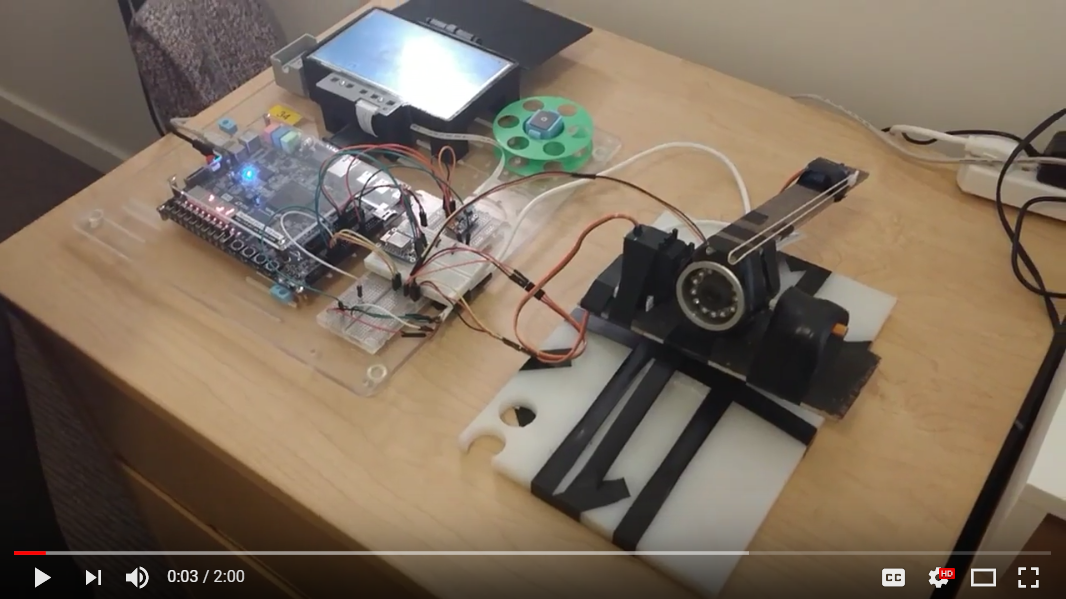
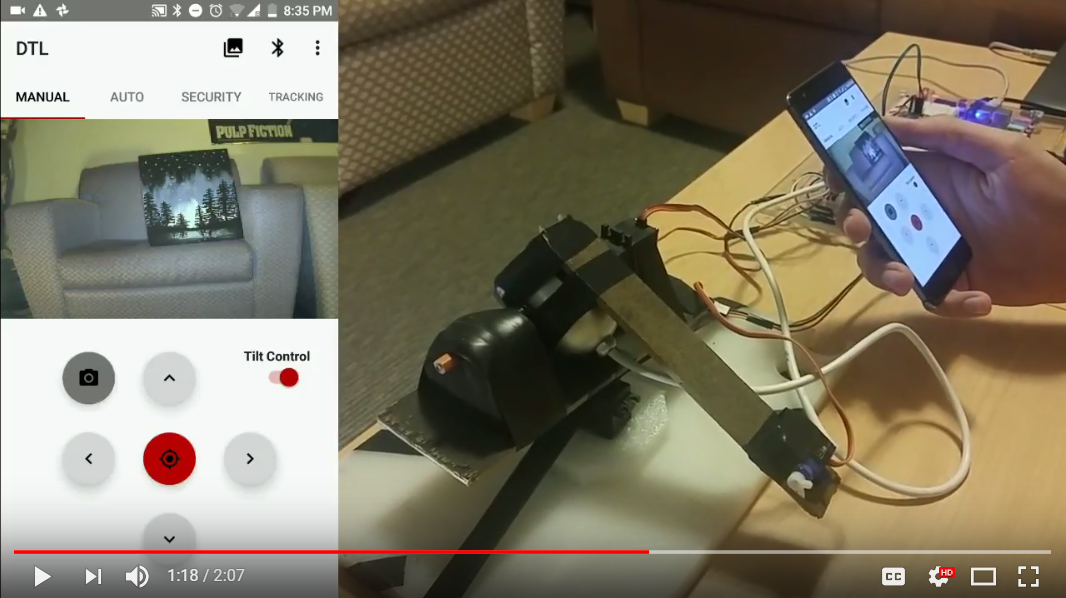
The DesktopLauncher is a toy turret that can aim, take photos, and be fired by the user. The DesktopLauncher was created using an FPGA as well as several other hardware components (servos, camera, bluetooth chip, touchscreen). Aside from the controls available on the turret’s touchscreen, users can pair the turret to an Android companion app. This Android app provides all the functionality of the turret alone, and adds several features that make it even more fun to play with.
This page shows how the development of the DesktopLauncher progressed over the course of 4 months and includes source code, design documentation, and demo videos.
Repository Structure
Three repositories make up the source code for Desktop Launcher
Module 1 - Core Functionality
In the first part of the DesktopLauncher project we wanted to create a version of the turret that had all of the core features and would work as an early proof of concept for the final app-enabled design. We started with an Altera DE1-SoC FPGA board onto which we loaded a Nios II processor capable of running programs written in C. In order to interface with other hardware that we would need to build the DesktopLauncher, we created low level Verilog and C communication libraries; to control the servos that would aim the turret synthesized a circuit that would generated a pulse-width modulated signal. A similair process was used to allow for communication with the camera, touchscreen, and display. After this we created a user-friendly GUI that allowed the user to aim, take photos, and fire the turret by tapping on the touchscreen. The final task of module 1 was to add mode functionality; the Desktop Launcher can operate in manual mode, automatic (where the turret scans the room while taking photos) and security mode (which waits and then fires when it detects motion).
Documentation for Module 1
Demo Video for Module 1
Module 2 - Extended Functionality
The second phase of our project centered around creating and incorporating an android app that could be connected via Bluetooth when the turret was put into pairing mode. The first aim of this module was to export all of the functionality of module 1 onto the mobile app and control the turret through Bluetooth. This included the basic rotation, firing, image capturing and displaying, and motion detection discussed previously. Once this core functionality and communication structure was established between the turret and the mobile app, additional features were added.
These included:
- Utilizing the Android device’s accelerometer to detect phone tilt and move the turret accordingly.
- Ability to tap on an image and have the turret rotate to center on that spot.
- A custom photo gallery to view photos taken by the turret.
- A settings menu to customize turret speed and photo settings.
- A tracking mode able to track a coloured blob as specified by the user.